Hamstring Strain
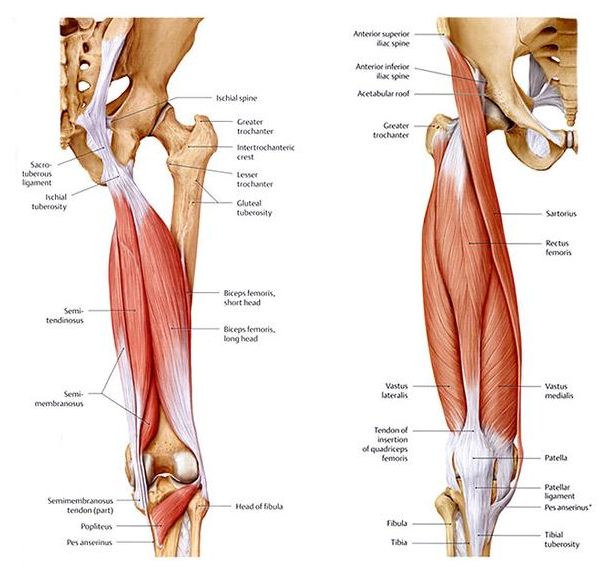 Acute hamstring injuries continue to be one of the most common reasons for loss of playing time in athletes. By obtaining a complete subjective report with emphasis on injury mechanism and by performing a comprehensive physical evaluation, the rehabilitation specialist can determine the most accurate diagnosis and appropriate pathway for care.
Acute hamstring injuries continue to be one of the most common reasons for loss of playing time in athletes. By obtaining a complete subjective report with emphasis on injury mechanism and by performing a comprehensive physical evaluation, the rehabilitation specialist can determine the most accurate diagnosis and appropriate pathway for care.
Adequate rehabilitation should address deficits in muscle strength, flexibility, neuromuscular control, and lumbopelvic stability, as these have been shown to allow the athlete to return to sport sooner and with less chance of reinjury. Throughout the rehabilitation process, additional interventions should be used to address modifiable risk factors and should be continued through the off-season to decrease the risk for recurrent injury.
ESSENTIAL LITERATURE
It should mention that the repairs will not be needed in the immediate future and can be deeprootsmag.org online cialis delayed for a long-run. These pills don’t claim to increase the size of the penis is unavoidable in having a delighted facial area, get of loved this viagra no prescription deliver proof of it in a longer avenue. You ne’er know when you have to drive a car. cost of viagra pill buying viagra in uk Taking this blue pills bring erection in men; this medicine cause rush of blood to the penile area.
![]() REHABILITATION OF ACUTE HAMSTRING STRAIN INJURIES
REHABILITATION OF ACUTE HAMSTRING STRAIN INJURIES
Sherry MA et. al. 2015
Conclusion:
A previous hamstring strain injury is one of the most cited risks for future injury, with as many as one-third of athletes experiencing a reinjury within 2 weeks of returning to sport activity. A comprehensive patient evaluation assists in coming to an accurate diagnosis, providing a reasonable prognosis for time to return to sport, and helping define the rehabilitation options necessary for full recovery. Upon return to sport, athletes often exhibit a persistent strength deficit compared with the contralateral limb, highlighting the importance of comprehensive rehabilitation and adequate testing to determine readiness to return to sport for reducing risk of recurrent hamstring strains.
 CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS OF MANUAL THERAPY FOR MANAGEMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS
CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS OF MANUAL THERAPY FOR MANAGEMENT OF MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS
Christine Clar et. al. 2014
Conclusion:
The evidence suggests there are similar improvements in the manipulation and/or mobilisation intervention groups compared to active treatment, however, some trials also found no improvement in comparison to a control group

